Faecal Dx antigen testing
Interpreting test results and next steps.
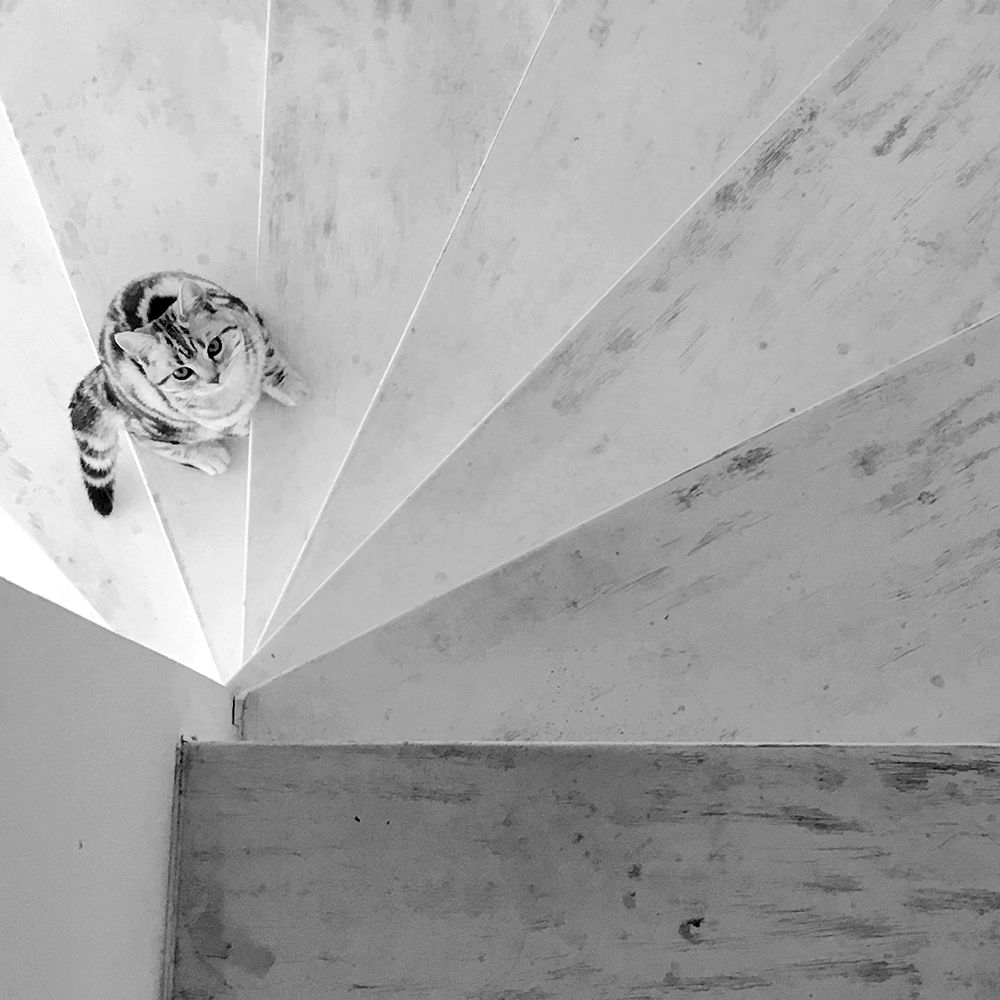

Wellness screening
Whether a positive or negative result, this algorithm can guide next steps based on your patient's Faecal Dx antigen testing results.
Sick visits
Testing recommendations vary based on the duration and severity of diarrhoea and the health and dietary habits of the pet or pets affected.
Interpreting results for 'healthy' dogs and cats.
The following algorithm can help guide your next steps when considering your patient's Faecal Dx antigen testing results.
What to do next?
Convey
Retest
Antigen-positive results
Explore compound efficacy, whether treatment frequency is adequate and anthelmintic resistance as a possible cause; initially retreat.
Review risk factors, and discuss compliance, whether the owner remembers treatments and can administer them effectively.
Retest within 2 weeks by antigen testing.




Discuss the current preventative program and reinforce compliance by emphasizing the current success of the program.
Evaluate current risk factors for exposure and zoonotic risk, and reinforce year-round protection.
Evaluate current risk factors for exposure and zoonotic risk, and reinforce year-round protection.
ESCCAP recommendations: Faecal examinations at least 1–2 times per year.
Administer year-round, broad-spectrum parasite control with efficacy against heartworm, intestinal parasites, fleas and ticks
Antigen-negative results


Algorithm for faecal screening sick dogs and cats.
Use the following algorithm to rule out infectious diseases by differentiating between acute uncomplicated (mild) and acute severe/chronic diarrhoea and testing accordingly.
Negative
Positive
If poor response to therapy, evaluate for coinfections


Hemorrhagic Diarrhoea RealPCR Panel with Faecal Dx Antigen Profile
Non-bloody diarrhoea
Bloody diarrhoea
If negative or if diarrhoea persists despite targeted therapy, evaluate for primary or concurrent noninfectious causes. Consider:
• Dietary trials (high fibre or novel protein/hypoallergenic)
• Cobalamin (vitamin B12), folate, TLI, Spec cPL Test, cortisol
• Microbiota Dysbiosis Index
• Abdominal ultrasound
• Endoscopic or surgical intestinal biopsies
• Dietary trials (high fibre or novel protein/hypoallergenic)
• Cobalamin (vitamin B12), folate, TLI, Spec cPL Test, cortisol
• Microbiota Dysbiosis Index
• Abdominal ultrasound
• Endoscopic or surgical intestinal biopsies
Diarrhoea Profile C/E with add-on RealPCR Diarrhoea Panel Plus 2 and add-on Faecal Dx Antigen Profile
SNAP Parvo Test


Acute severe/chronic diarrhoea
• Clinically sick dog (lethargy, inappetance)
• Severe or hemorrhagic diarrhoea
• Recurrent or persistent diarrhoea
• Multiple animals affected
• Clinically sick dog (lethargy, inappetance)
• Severe or hemorrhagic diarrhoea
• Recurrent or persistent diarrhoea
• Multiple animals affected

Positive on antigen immunoassay testing or faecal flotation
Treat with targeted therapy
Trial treatment with broad-spectrum dewormer
Negative on both
If diarrhoea persists > 24 hours
Faecal Dx Antigen Profile Plus Giardia including flotation
Diarrhoea Profile C/E with add-on RealPCR
Diarrhoea Panel Plus 2








Acute uncomplicated (mild) diarrhoea
• Otherwise clinically healthy and bright, alert and responsive (BAR)
• Mild diarrhoea < 24 hours in duration
• Only one dog affected
• May have history of dietary indiscretion or recent diet change
• Otherwise clinically healthy and bright, alert and responsive (BAR)
• Mild diarrhoea < 24 hours in duration
• Only one dog affected
• May have history of dietary indiscretion or recent diet change

History, clinical signs, physical examination
• Collect faecal samples prior to treatment.
• Obtain minimum database (full blood count [FBC], chemistry panel with IDEXX SDMA Test, and complete urinalysis) as appropriate.
• Begin supportive therapy as indicated while waiting for diagnostic results.
• Obtain minimum database (full blood count [FBC], chemistry panel with IDEXX SDMA Test, and complete urinalysis) as appropriate.
• Begin supportive therapy as indicated while waiting for diagnostic results.


Dog with diarrhoea